1. Introduction
Why Build a Smart Home?
A smart home can transform daily life, creating a connected environment that responds to your needs, optimizes energy use, and increases security. Smart technology allows you to integrate lighting, climate control, security systems, and entertainment in a way that enhances comfort, safety, and efficiency.
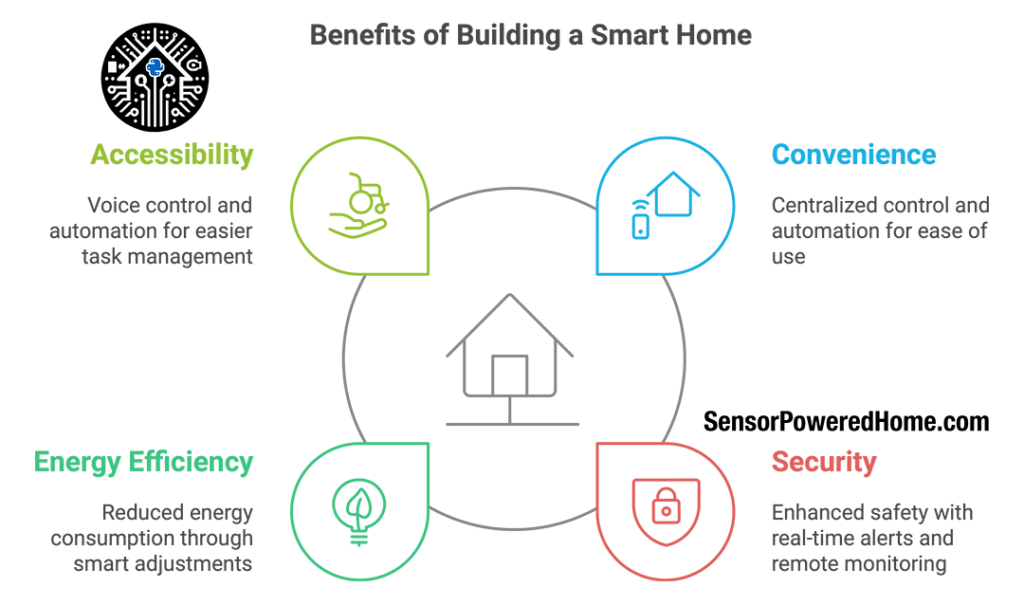
Here are the main benefits of building a smart home:
- Convenience: Smart home technology brings many essential controls into one place, often accessible through a single app or even voice commands. With automation, you can set routines, such as turning on the lights when you enter a room or starting the coffee maker each morning.
- Security: Smart home devices can provide real-time security alerts and allow you to monitor your home remotely. Security systems with cameras, motion sensors, and smart locks can work together to create a safer environment, giving you peace of mind.
- Energy Efficiency: Smart home systems can automatically adjust lighting, heating, and appliance use to reduce energy consumption, helping you save on utilities while also lowering your carbon footprint.
- Accessibility: For those with limited mobility or other disabilities, smart technology offers voice control and automation features that make everyday tasks easier. Accessibility-focused options allow you to control lights, locks, and more without needing to physically interact with them.
Overview of the Guide
This guide will take you through every step of planning and building a smart home. Here’s what you can expect to learn:
- The Basics of Smart Home Technology: An overview of the essential components that make up a smart home.
- DIY and Open-Source Options: Cost-effective, customizable solutions using platforms like openHAB and Home Assistant, along with a comparison of DIY and commercial devices.
- Step-by-Step Setup and Automation: Guidance on selecting, installing, and integrating devices to create routines and automations.
- Budgeting and Expansion Tips: Insights on balancing costs with functionality, including a cost comparison for DIY vs. commercial devices and tips for future scalability.
Whether you’re interested in DIY, commercial options, or a mix of both, this guide will help you build a smart home that aligns with your goals.
2. Defining Your Smart Home Goals
Now that you know what a smart home can offer, it’s time to define your specific goals. This section will guide you in identifying the features that matter most to you and help you create a customized smart home plan.
Assessing Your Needs and Priorities
To create a smart home that truly enhances your lifestyle, it’s essential to start by identifying your top priorities. Here’s how to assess your needs in key areas:
- Security: If protecting your home is your main goal, focus on smart locks, cameras, motion detectors, and alarm systems. Together, these devices can provide a secure environment with real-time alerts and remote monitoring. You’ll want to prioritize security-focused devices if peace of mind and remote access are essential to you.
- Energy Savings: For readers interested in reducing energy consumption, smart thermostats, lighting, and appliance controls are ideal. These devices help manage your home’s electricity and heating usage more efficiently, potentially lowering your energy bills. If energy efficiency is a priority, look for devices that can adjust based on occupancy and time of day.
- Convenience: If simplifying daily routines is a top goal, look for voice-controlled hubs, automated lighting, and connected appliances. Convenience-driven smart homes aim to make everyday tasks easier, often automating repetitive actions. If the idea of a home that responds to your habits appeals to you, prioritize convenience-focused devices.
- Entertainment: For entertainment enthusiasts, a smart home can create a seamless audio-visual experience. Smart TVs, home theater systems, and multi-room audio setups let you enjoy music, movies, and more without extra setup or manual controls. If you value high-quality entertainment experiences, consider entertainment-focused smart home setups.
Choosing one or two primary goals will help you avoid overwhelming your system with too many new features and create a smart home experience that meets your specific needs.
Creating a Wish List
Once you’ve defined your priorities, draft a wish list of devices or features that align with those goals. This list will serve as your roadmap as you explore options, helping you stay focused on what truly matters. Here’s an example of how you might organize your wish list based on different goals:
- Security:
- Front door security camera
- Smart door locks with remote control
- Window and door sensors
- Motion-activated outdoor lights
- Energy Savings:
- Smart thermostat with learning capabilities
- Energy-efficient smart bulbs with remote dimming
- Smart plugs with energy monitoring features
- Solar-powered outdoor lights
- Convenience:
- Voice-controlled hub (e.g., Alexa, Google Assistant)
- Routine lighting for daily activities (e.g., morning wake-up, evening wind-down)
- Smart coffee maker integrated with a morning routine
- Automated shades to close at night
- Entertainment:
- Smart TV with voice control and streaming options
- Multi-room audio system for music in every room
- Media server for easy access to movies and shows
- Gaming console integration with lighting and audio effects
With your wish list ready, you can begin prioritizing items based on factors such as budget, ease of installation, and compatibility with existing devices. This will guide you as you start selecting the right components for your smart home, ensuring you focus on features that match your goals.
In the following sections, we’ll explore the core components of a smart home and how to select the devices that best fit your priorities.
3. Understanding Smart Home Components
Building a smart home involves more than just buying gadgets; it’s about creating a cohesive system where each device plays a specific role, enhancing your home’s functionality and adapting to your lifestyle. In this section, we’ll cover the core components of a smart home, the main categories of devices, and practical budgeting tips that include both DIY and commercial options.
Overview of Core Smart Home Components
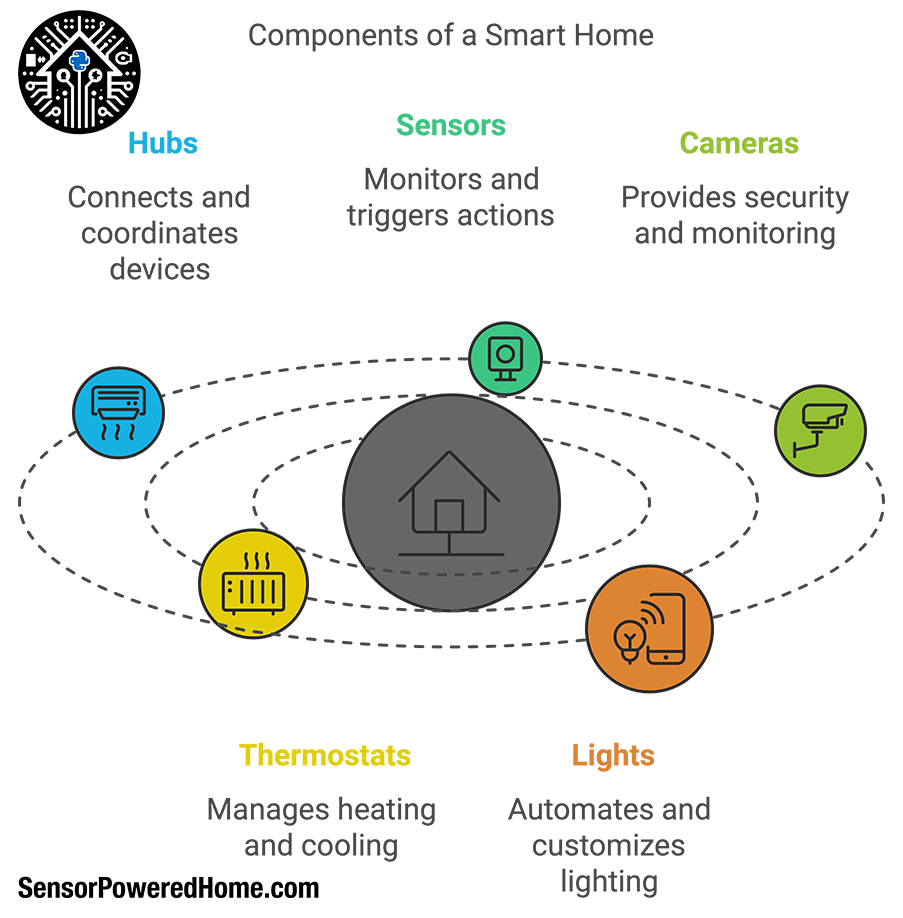
Smart home technology is built around several core components, each serving a distinct function within the system. Here’s a look at some of the primary device types you’ll encounter when planning a smart home setup:
- Hubs: A hub is often considered the “brain” of a smart home system, connecting and coordinating various devices across different brands or platforms. Hubs allow devices to communicate seamlessly, enabling centralized control through a single app or voice assistant. While some smart devices can operate independently, hubs are particularly useful when managing multiple devices that need to work together, such as creating a security or climate control routine.
- Sensors: Sensors are essential for monitoring and triggering actions within the smart home. These include motion sensors for detecting presence, door/window sensors for security, temperature and humidity sensors for climate control, and even sensors that monitor air quality. Sensors add “intelligence” to your smart home by providing data that can be used to activate devices automatically, based on specific conditions.
- Cameras: Cameras enhance security and convenience, offering real-time monitoring and recording of specific areas in or around your home. Smart cameras often come with additional features like motion detection, two-way audio, and night vision. These cameras can be accessed remotely, allowing you to keep an eye on your home no matter where you are.
- Thermostats: Smart thermostats manage your home’s heating and cooling systems to improve energy efficiency and comfort. These thermostats can learn your schedule, adjust temperatures based on occupancy, and allow remote control via smartphone. Many smart thermostats integrate with other devices, such as sensors that detect room occupancy, to adjust climate settings automatically.
- Lights: Smart lighting systems let you control and automate lights throughout your home, often through voice commands, smartphone apps, or motion sensors. They’re a popular entry point into smart home technology due to their ease of setup and immediate impact. From smart bulbs to wall-mounted dimmers, these devices allow you to customize lighting according to mood, schedule, or occupancy.
Categories of Smart Home Devices
To create a functional and harmonious smart home, it’s helpful to understand the different device categories and their typical roles within the system. Here are the primary categories:
- Security Devices: Security-focused devices like cameras, motion detectors, and smart door locks are designed to keep your home safe. These devices can alert you to unexpected activity, lock or unlock doors remotely, and provide video monitoring, allowing you to maintain security even when you’re away. Many security devices are designed to work in tandem with one another, creating a comprehensive security system that automatically activates when you leave home or at specific times of day.
- Climate Control Devices: Smart thermostats and HVAC integrations give you precise control over your home’s temperature and air quality. For example, a smart thermostat can be programmed to maintain different temperatures in different zones or at various times, which can help reduce energy costs. HVAC integrations with humidity or CO2 sensors can also monitor and improve indoor air quality, contributing to a healthier living environment.
- Lighting Devices: Smart bulbs, switches, and dimmers offer a flexible approach to lighting control. You can adjust brightness, color, and scheduling through an app or voice command. Automated lighting helps conserve energy and enhance security by giving the impression someone is home even when the house is empty. Lighting is also a key component in creating personalized routines, such as dimming lights for relaxation or brightening them to help you wake up.
- Entertainment Devices: Smart speakers, TVs, and media hubs bring entertainment to the next level by integrating streaming services, voice controls, and multi-room audio. For instance, a smart speaker like an Amazon Echo or Google Nest can play music, control compatible devices, and answer questions, all with voice commands. Meanwhile, media hubs allow centralized access to streaming services, creating a seamless and enjoyable entertainment experience.
- Utility and Appliance Devices: Devices like smart plugs, outlets, and kitchen appliances extend smart home technology’s reach into daily tasks. Smart plugs can turn traditional appliances into smart devices, giving you remote control over their on/off functions. Advanced appliances, such as smart refrigerators or coffee makers, allow you to automate daily tasks and monitor appliance status, saving you time and adding convenience.
Budgeting for Your Smart Home
When it comes to budgeting, it’s essential to consider not only the initial purchase price but also ongoing maintenance and potential upgrade costs. Many people assume smart home setups are prohibitively expensive, but there are options for every budget, especially if you’re open to DIY solutions.
- Initial Costs: The cost of setting up a smart home varies widely based on the scope and complexity of the system you envision. A basic setup with a few lights, a smart speaker, and a thermostat may cost a few hundred dollars, while a full-home system with cameras, climate control, security, and entertainment features could run into the thousands. Initial costs are higher for commercial devices that come ready-made and usually include support and updates.
- Ongoing Maintenance: Some devices require ongoing maintenance, like battery replacements for sensors or subscription fees for advanced security camera features. Maintenance costs may also include software updates or occasional repairs, which can add up over time, especially for high-end systems. DIY systems based on open-source platforms like openHAB and Home Assistant typically have lower ongoing costs, as they don’t rely on subscription-based services and can be updated and maintained independently.
- Upgrade Considerations: Smart home technology evolves rapidly, so it’s wise to anticipate upgrade costs. Some homeowners start with a few core devices and gradually add others, spreading the investment over time. Choosing scalable technology—devices that can grow with your needs—ensures you won’t need to replace equipment frequently. Open-source platforms like Home Assistant allow for more flexibility in upgrades, as they integrate easily with a variety of device brands and new technologies.
DIY is Feasible
If you’re technically inclined, DIY is a practical way to build a cost-effective smart home. DIY solutions offer significant savings and customization flexibility. With open-source platforms like openHAB and Home Assistant, you can integrate a wide range of sensors and devices without being limited to a single brand. Here’s a look at some DIY options:
- Sensors and Actuators: DIY sensors can include motion detectors, temperature and humidity sensors, and light sensors. Actuators, like smart switches or relays, allow you to control connected devices manually or through automation. These can often be sourced individually and configured with platforms like Home Assistant, which supports numerous protocols, including Zigbee and Z-Wave.
- Open-Source Platforms: Both Home Assistant and openHAB are widely used, open-source smart home platforms that allow you to control devices and create automation routines without relying on a centralized commercial ecosystem. They support integration with hundreds of devices, providing a budget-friendly solution with no subscription fees.
Cost Comparison Table
Below is a comparison of typical costs for DIY vs. commercially available sensors, actuators, and platforms, highlighting where savings can be achieved:
| Component | DIY Cost Range | Commercial Cost Range | Savings with DIY |
|---|---|---|---|
| Motion Sensor | |||
| Smart Thermostat | |||
| Smart Light Bulb | |||
| Security Camera | |||
| Open-Source Platform | Free |
With DIY, you can significantly cut costs by selecting individual components and assembling them yourself. However, DIY solutions require more technical knowledge and time for setup, while commercial devices offer easier installation and support. Ultimately, a combination of both approaches allows for a flexible, cost-effective smart home setup tailored to your needs.
In the following section, we’ll explore different smart home platforms and how to choose one that meets your goals and works well with your devices.
4. Choosing a Smart Home Platform
Choosing the right smart home platform is one of the most crucial steps in building a functional and user-friendly system. A platform serves as the control center of your smart home, linking various devices and enabling centralized control through a single app or voice assistant. This section will provide an overview of popular platforms, guide you on assessing device compatibility, and offer insight into balancing ease of use with customization.
Popular Platforms and Their Pros & Cons
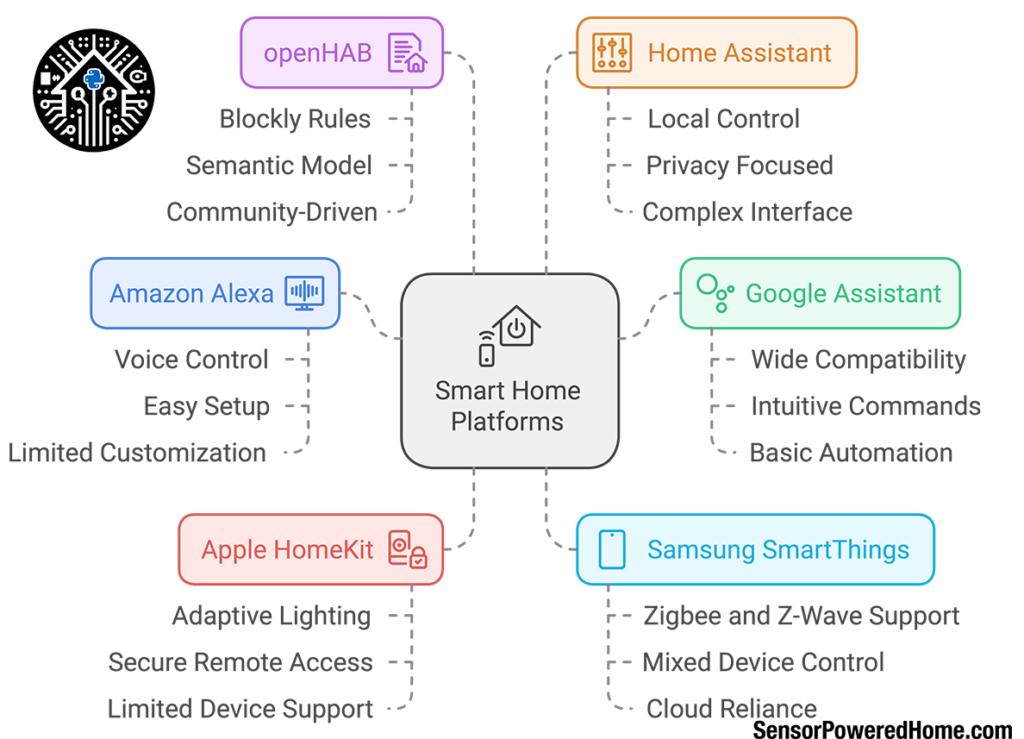
Several platforms dominate the smart home landscape, each offering unique features, integrations, and levels of control. Here’s an overview of the most popular options, including open-source solutions like openHAB and Home Assistant.
- Amazon Alexa: Known for its compatibility with a vast array of smart devices, Alexa is a popular choice for its accessibility and ease of use. Alexa-enabled devices are easy to set up and offer voice control for compatible products, but Alexa’s functionality may be limited for users who need advanced customization.
- Google Assistant: Google Assistant is another widely compatible option, with integration across smart speakers, phones, and displays. It excels at natural language processing, making voice commands intuitive and responsive. Google Assistant is a solid choice for beginners and integrates well with Google’s ecosystem, though it may lack the advanced automation and custom rules found in open-source options.
- Apple HomeKit: Apple’s HomeKit platform prioritizes privacy and security, making it appealing for users deeply invested in Apple’s ecosystem. With features like adaptive lighting and secure remote access through iCloud, HomeKit offers a seamless experience for iOS users. However, HomeKit-compatible devices are somewhat limited compared to other platforms, and users outside of Apple’s ecosystem may find it restrictive.
- Samsung SmartThings: SmartThings offers broad compatibility with various devices and brands, allowing users to control devices from multiple ecosystems through one app. It supports Zigbee and Z-Wave protocols, making it a good option for mixed device environments. While user-friendly, SmartThings’ reliance on a cloud-based infrastructure can limit control and speed.
- openHAB: openHAB (Open Home Automation Bus) is a powerful open-source platform that supports hundreds of device integrations across multiple protocols. It’s especially suitable for beginners, thanks to its Blockly Rules and Semantic Model. The Blockly Rules feature uses a visual, block-based programming system, allowing users to create automation rules without coding experience. The Semantic Model further simplifies device organization by categorizing and structuring devices based on their locations and functions. This intuitive setup, combined with a community-driven ecosystem, makes openHAB a flexible and accessible platform for both beginners and advanced users.
- Home Assistant: Another open-source platform, Home Assistant provides extensive customization and integration options, supporting over a thousand devices and services. It requires some technical knowledge for initial setup but offers unparalleled flexibility. With local control and privacy-focused design, Home Assistant is ideal for users who want to keep their data secure and have full control over automation. However, its complex interface may be overwhelming for beginners.
For a deeper dive into these platforms, see our related article: Introduction to Home Automation Apps for Beginners.
Assessing Compatibility with Existing Devices
One of the first things to consider when choosing a platform is compatibility with your existing devices. Each platform has unique integrations and may support certain devices better than others. Here’s how to ensure compatibility:
- Device Ecosystem: If you already own smart devices, check the compatibility lists provided by each platform to see which ones work seamlessly. For example, Alexa and Google Assistant have broad compatibility with numerous brands, while Apple HomeKit is more limited to Apple-certified devices.
- Communication Protocols: Platforms may support different communication protocols, such as Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Z-Wave, or Bluetooth. SmartThings, for example, supports both Zigbee and Z-Wave, which makes it compatible with a wide variety of smart home devices. For users interested in open-source options, both openHAB and Home Assistant support a broad range of protocols, making them adaptable for future expansions.
- Long-Term Integration: Consider how well each platform will support future additions. Open-source platforms like openHAB and Home Assistant are particularly strong in this regard, as they have a dedicated community constantly adding new device integrations. Commercial platforms may be limited by proprietary ecosystems or require updates from the manufacturer for new device support.
Ease of Use vs. Customization
When selecting a platform, balancing ease of use with customization is essential, especially if you’re a beginner. Each platform offers different levels of control and complexity, and your choice should align with your comfort level and automation goals.
- Beginner-Friendly Platforms: Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple HomeKit are all highly accessible for beginners. These platforms offer straightforward setup processes, intuitive apps, and voice control for easy operation. However, they are generally limited in customization, with fewer options for advanced automations and personalized rules.
- Customizable Platforms: For those looking to create highly customized smart home systems, open-source options like openHAB and Home Assistant provide the flexibility to configure advanced automations, integrate a broad range of devices, and even run local control. With openHAB’s Blockly Rules, beginners can create custom automations using a simple drag-and-drop interface, making it accessible without sacrificing customization. The Semantic Model in openHAB also organizes devices in a logical structure, making navigation and management easier for users of all experience levels.
- Hybrid Options: Samsung SmartThings strikes a balance between beginner-friendly and customizable. While offering an easy setup and app control, SmartThings also provides more options for creating routines and linking devices than platforms like Alexa or Google Assistant. It’s a good choice for users who want more control without delving into complex setups.
In summary, your platform choice should align with your current needs and technical comfort level, while also allowing for future growth. Beginners may appreciate the user-friendly interfaces of commercial platforms, but for those seeking a blend of accessibility and power, open-source options like openHAB—with its Blockly Rules and Semantic Model—provide a unique combination of simplicity and customization.
5. Planning Your Smart Home Network
Setting up a reliable network is fundamental for any smart home, as it ensures seamless communication between devices, reduces connection drops, and maintains the security of the entire system. The following summaries provide insights from two articles that offer essential network planning tips for smart home users.
Executive Summary of Network Essentials
Article Summary: Building a Reliable Smart Home Network – Part 1
This article introduces the basics of setting up a stable network infrastructure specifically tailored for smart homes. It covers critical network requirements and best practices for optimizing router placement and reducing interference from other electronic devices. It explains how smart homes require reliable, high-speed internet to support multiple connected devices and highlights the importance of positioning routers centrally and away from physical obstructions to enhance Wi-Fi coverage. The article also provides practical tips on selecting routers with the latest standards, such as Wi-Fi 6, which offers faster speeds and better device handling capabilities for smart home applications.
Key Takeaways from Part 1:
- Optimal Router Placement: Place routers centrally, on elevated surfaces, and away from interference to maximize Wi-Fi coverage.
- Choosing the Right Router: Use routers that support the latest Wi-Fi standards (Wi-Fi 6) to handle multiple devices effectively.
- Managing Bandwidth: Prioritize bandwidth for critical smart devices and allocate network resources to avoid congestion.
Article Summary: Building a Reliable Smart Home Network – Part 2
The second part delves into more advanced networking options for larger homes or setups with numerous devices. It explains the benefits of mesh Wi-Fi systems, which use multiple nodes to extend coverage evenly across the home, and discusses the use of VLANs (Virtual LANs) to create segmented networks. VLANs are especially valuable in smart homes because they allow users to separate IoT devices from personal devices, enhancing security by isolating potential vulnerabilities in IoT connections. This article emphasizes the need for WPA3 encryption to protect data from unauthorized access, offering a guide to setting up secure networks.
Key Takeaways from Part 2:
- Mesh Wi-Fi for Larger Homes: Mesh Wi-Fi extends coverage seamlessly across larger areas and reduces dead zones.
- VLANs for Improved Security: Segmenting networks with VLANs isolates IoT devices from personal data, minimizing security risks.
- WPA3 Encryption: Enabling WPA3 provides the latest encryption standard to protect data on the smart home network.
Security Measures for a Smart Home Network
Smart home networks are particularly vulnerable to security threats due to the large number of connected devices. The articles emphasize the importance of network segmentation (using VLANs) to separate IoT devices from primary devices, significantly reducing potential attack vectors. They also stress the need for WPA3 encryption, which is currently the most secure Wi-Fi encryption standard, to protect user data. Additionally, setting up a separate network for IoT devices ensures that even if one device is compromised, it does not expose personal data on the main network.
In summary, a well-planned network infrastructure not only supports smart home devices but also secures them. The articles underscore the value of mesh Wi-Fi systems for consistent coverage, VLANs for device segmentation, and WPA3 encryption for optimal security, providing a strong foundation for a smart home network that balances performance with protection.
6. Selecting and Installing Core Devices
When building a smart home, selecting core devices such as hubs, lights, thermostats, cameras, and voice assistants is essential to achieve a seamless, efficient setup. DIY options, while requiring more time and a learning curve, benefit from a robust and active community. Resources and community forums offer invaluable help, guiding beginners through setup and troubleshooting challenges. In this section, we’ll cover popular commercial and DIY options, detailing pros, cons, prices, and setup difficulty.
Smart Hubs and Controllers
A smart hub is the central controller of a smart home, connecting and automating various devices. Here’s a look at some top choices:
- Samsung SmartThings Hub
Pros: Broad compatibility with Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Wi-Fi devices, making it easy to integrate with products across multiple brands. Simple automation options are available, and it integrates well with Alexa and Google Assistant.
Cons: Relies on cloud connectivity, which can introduce latency and raises security concerns.
Price: Approximately 100
100
Setup Difficulty: Very easy, with guided setup through the Alexa app. - DIY Hub with Raspberry Pi and openHAB
Pros: Highly customizable, supports various devices, and offers local control, enhancing privacy and reducing latency. Thanks to openHAB’s Blockly Rules (a visual rule editor) and Semantic Model (an organization tool for devices), it’s a beginner-friendly platform for those who want DIY flexibility. Installing openHAB on Raspberry Pi is straightforward by following the official guide: openHAB Installation Guide. Using the openHABian image, you can easily set up openHAB on a Raspberry Pi with little prior experience.
Cons: Requires time to configure and familiarize oneself with openHAB’s ecosystem, though community support and resources are readily available to help.
Price: Raspberry Pi kits start at 120
120Easy Amazon Echo with Alexa Voice assistant, simple setup Alexa ecosystem limitations 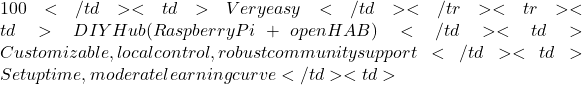 70
70Learning curve, longer setup Smart Lights
Smart lighting includes bulbs and switches that can be controlled remotely and automated. Here are some options:
- Philips Hue Bulbs
Pros: Known for high-quality color options and reliable control, compatible with Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple HomeKit.
Cons: Higher cost compared to other brands; requires a Philips Hue Bridge for full functionality.
Price: Starts at 25 per bulb.
25 per bulb.
Setup Difficulty: Very easy; setup via the LIFX app. - DIY LED Strip Lighting with ESP8266, Configured with openHAB
Pros: Fully customizable, affordable, and ideal for users who enjoy hands-on projects. These LED strips can be automated through openHAB, enabling dynamic lighting control.
Cons: Requires knowledge of electronics and programming, longer setup and configuration time, and familiarity with openHAB integration.
Price: Approximately 15+
15+Easy LIFX Bulbs No hub required, vibrant colors Wi-Fi-only, costly 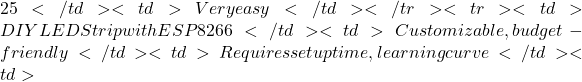 15
15Learning curve, longer setup Smart Thermostats
Smart thermostats provide precise climate control with scheduling and remote access options, making them ideal for energy efficiency. Here are some options:
- Google Nest Thermostat
Pros: Learns user habits to adjust temperatures automatically, integrates well with Google Assistant and Alexa, and is energy-efficient.
Cons: Higher initial cost, with some advanced features behind a subscription paywall.
Price: Ranges from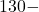 250 depending on the model.
250 depending on the model.
Setup Difficulty: Moderate; may require professional installation if wiring is complex. - Ecobee SmartThermostat
Pros: Comes with a room sensor for optimal temperature control, built-in Alexa voice control, and compatibility with multiple smart platforms.
Cons: High price point and somewhat complex interface.
Price: Around 30 for components.
30 for components.
Setup Difficulty: Learning curve involved with programming and setup, but extensive community support is available.
Smart Thermostats Comparison Table
Thermostat Pros Cons Price Setup Difficulty Google Nest Thermostat Energy-efficient, learns habits Higher cost, subscription needed 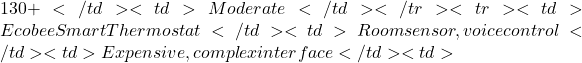 250
250Moderate DIY ESP32 Thermostat Customizable, openHAB-compatible Setup time, learning curve 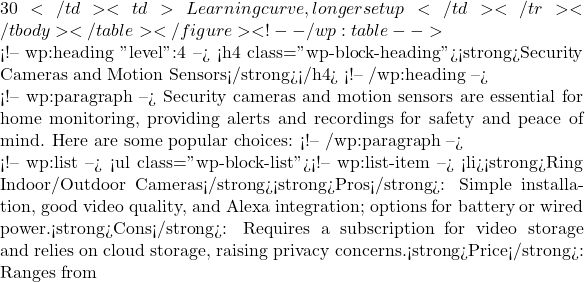 60-
60- 200 per camera.
200 per camera.
Setup Difficulty: Moderate; requires good Wi-Fi coverage for best performance.- DIY Security Camera with Raspberry Pi and openHAB
Pros: Cost-effective, customizable, with local storage options, and integration with openHAB for full automation.
Cons: Requires assembly and configuration, lower video quality than commercial options, and longer setup and configuration time.
Price: Approximately 60-
60- 200 | Moderate |
200 | Moderate |
| DIY Raspberry Pi Camera | Customizable, budget-friendly, openHAB compatible | Setup time, learning curve | 80.
80.
Setup Difficulty: Very beginner-friendly; quick setup via Alexa app.- Google Nest Audio
Pros: High-quality sound, excellent integration with Google services, and responsive to natural language commands.
Cons: Limited to Google ecosystem, requires Wi-Fi for functionality.
Price: Approximately 50.
50.
Setup Difficulty: Learning curve and longer setup; requires openHAB integration and assembly.Voice Assistants and Smart Speakers Comparison Table
Device Pros Cons Price Setup Difficulty Amazon Echo Easy setup, broad compatibility Alexa ecosystem limitations  100
100Very easy DIY Speaker (Raspberry Pi) Customizable, privacy-focused Setup time, limited features  100-
100- 300-
300- 600 and up): A full-featured setup might involve a smart hub, several smart lights, sensors (motion, door/window), and smart security cameras. This setup allows you to automate routines and integrate devices across multiple rooms for a robust experience.
600 and up): A full-featured setup might involve a smart hub, several smart lights, sensors (motion, door/window), and smart security cameras. This setup allows you to automate routines and integrate devices across multiple rooms for a robust experience.DIY options can reduce costs, especially if you build components or use open-source platforms like openHAB or Home Assistant, which allow greater customization without recurring fees.
Q4: How to secure smart home devices?
Securing smart home devices is essential to protect your privacy and prevent unauthorized access. Here are best practices for keeping your system secure:
- Use Strong, Unique Passwords: Set unique passwords for each device, hub, and app. Avoid using default passwords, which are easy for attackers to guess. Consider using a password manager like LastPass to keep track of complex passwords.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): For accounts that offer it, enable 2FA to add an extra layer of protection. Services like Google and Amazon support 2FA, making it more challenging for unauthorized users to access your devices.
- Segment Your Network: Create a separate guest network for IoT devices, isolating them from your primary devices like computers and phones. Many routers support guest networks, which prevent potential hackers from accessing sensitive data if they breach one device.
- Disable Unnecessary Features: Turn off Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) and remote access unless needed, as these features can create vulnerabilities. Check your router settings and each device’s app to disable these features.
- Keep Firmware Updated: Regularly update device firmware and apps. Many updates include security patches that fix known vulnerabilities, protecting devices from the latest threats.
Q5: Can I set up a smart home if I’m not tech-savvy?
Yes, you can set up a smart home even if you’re not tech-savvy! Many smart home devices are designed for easy installation and use. Here are tips for beginners:
- Start Small: Begin with user-friendly devices like smart bulbs, plugs, or a voice assistant (Amazon Echo or Google Nest). These devices are typically easy to set up through simple apps.
- Use Pre-Configured Routines: Many apps, like Amazon Alexa and Google Home, offer pre-configured routines to get started with automation without needing technical knowledge.
- Join Supportive Communities: Forums like SensorPoweredHome.com, openHAB Community, and Reddit’s r/smarthome offer advice, answer questions, and provide step-by-step guides.
With patience and the right resources, anyone can start and enjoy the benefits of a smart home.
Q6: What are the pros and cons of using a voice assistant?
Voice assistants, like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri, offer convenience but have limitations and privacy considerations.
- Pros:
- Hands-Free Control: Use voice commands to control devices without needing a smartphone or remote.
- Quick Access to Information: Ask for weather updates, traffic, and news.
- Routine Automation: Voice assistants make it easy to set up routines and group multiple devices under a single command.
- Cons:
- Privacy Concerns: Voice assistants may inadvertently record conversations or use data for targeted ads.
- Limited Device Compatibility: Not all devices work with all assistants; ensure compatibility before buying.
- Dependence on Internet: Most voice assistants require internet connectivity, meaning they may not work if the network goes down.
To enhance privacy, review each assistant’s privacy settings to limit data sharing and disable features like microphone usage when not needed.
Q7: Can smart home devices increase my energy savings?
Yes, many smart home devices can help reduce energy consumption, potentially lowering utility bills. Here are some ways to achieve this:
- Smart Thermostats: Devices like the Google Nest or Ecobee SmartThermostat learn your habits and adjust temperatures based on occupancy, reducing heating/cooling costs by only activating when needed.
- Smart Lighting: Use smart bulbs or switches to automate lighting schedules, ensuring lights aren’t left on unnecessarily. For example, set lights to turn off during the day or when no motion is detected.
- Energy Monitors: Energy monitoring devices, such as the Sense Energy Monitor, provide real-time data on energy usage, helping you identify high-usage appliances and adjust behaviors to conserve energy.
Many of these devices offer tracking features so you can monitor your energy savings over time.
Q8: How reliable are smart home devices?
Most smart home devices are quite reliable, but they depend on factors like Wi-Fi connectivity, power supply, and compatibility. Here are some tips to improve reliability:
- Choose Reputable Brands: Opt for well-reviewed brands with good support, as they tend to provide more stable devices with regular firmware updates.
- Use a Mesh Wi-Fi Network: If your home has many devices or is large, a mesh Wi-Fi system can improve connectivity, ensuring each device has a strong signal.
- Have Backup Power: For critical devices, like security systems or smart locks, consider using a battery backup or UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) to keep them functioning during power outages.
If reliability issues persist, forums like openHAB Community and Home Assistant Community provide troubleshooting advice tailored to specific devices.
12. Conclusion
Building a smart home can be a fulfilling and transformative experience, enhancing convenience, security, and energy efficiency. Here’s a recap of the key points discussed throughout this guide, along with tips to ensure an enjoyable, rewarding journey.
Recap of Key Points
In this guide, we covered essential aspects of creating and maintaining a smart home system:
- Understanding Devices and Platforms: We explored the core components of a smart home, including lighting, thermostats, security devices, and hubs, as well as open-source platforms like openHAB and Home Assistant for deep customization.
- Automation and Routines: By learning the basics of automation—triggers, conditions, and actions—you can start creating routines that fit seamlessly into your daily life, from morning routines to energy-saving automations.
- Maintaining and Troubleshooting: A smooth-running smart home requires regular updates, occasional troubleshooting, and security best practices. Ensuring devices are secure and reliable is vital for long-term enjoyment.
- Scaling with MQTT and Seasonal Adjustments: As your system grows, protocols like MQTT enable flexible, efficient expansion. Seasonal adjustments, such as temperature regulation or holiday lighting, can adapt your smart home to changing needs throughout the year.
By applying these foundational concepts, you’re equipped to create a smart home that meets your unique needs and evolves as technology advances.
Encouragement for Starting Small
For beginners, the vast array of devices and options can feel overwhelming. Start small with essential devices like smart bulbs or a thermostat, gradually adding features as you gain confidence. Focus on simple automations at first, such as turning lights on at sunset or setting a morning coffee routine. With each success, you’ll become more comfortable and ready to take on more complex integrations and routines.
Remember, there’s no need to achieve everything at once. As you expand, you’ll discover what works best for your lifestyle, which helps guide future investments and customizations. Starting small also gives you time to adjust and explore options without a heavy initial cost.
Final Tips for an Enjoyable Smart Home Journey
Above all, enjoy the process of experimenting, learning, and gradually transforming your home. Here are a few parting tips for a satisfying smart home journey:
- Embrace Experimentation: Try new routines, adjust settings, and experiment with different devices and automations. Smart homes are highly customizable, and small tweaks can make a big difference in how well they fit your lifestyle.
- Tap into Community Support: Online communities, such as openHAB Community and Home Assistant Community, offer advice, inspiration, and solutions. Visiting these resources regularly can help you discover new ideas and solve problems as they arise.
- Keep Learning and Adapting: Smart home technology evolves quickly, with new devices and features emerging regularly. By staying curious and open to learning, you’ll be ready to take advantage of new opportunities to enhance your setup.
A smart home is more than just technology; it’s an opportunity to improve your living environment, enhance comfort, and enjoy more convenience every day. Embrace the journey, start small, and enjoy the endless possibilities of transforming your home into a smart, responsive environment that grows with you.
- Google Nest Thermostat
- Philips Hue Bulbs