How to Set Up Z-Wave and Zigbee Devices for Smart Homes
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Z-Wave and Zigbee Protocols
- Understanding the Basics of Z-Wave and Zigbee Devices
- Preparing for Setup
- Advanced Configuration Options
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Ensuring Network Security
- Real-World Use Cases
- Tools and Apps for Managing Z-Wave and Zigbee Networks
- Conclusion
- FAQ Section
1. Introduction to Z-Wave and Zigbee Protocols
Overview of Z-Wave and Zigbee Technologies
Z-Wave and Zigbee are the backbone of many smart home systems, each offering unique strengths that cater to different automation needs.
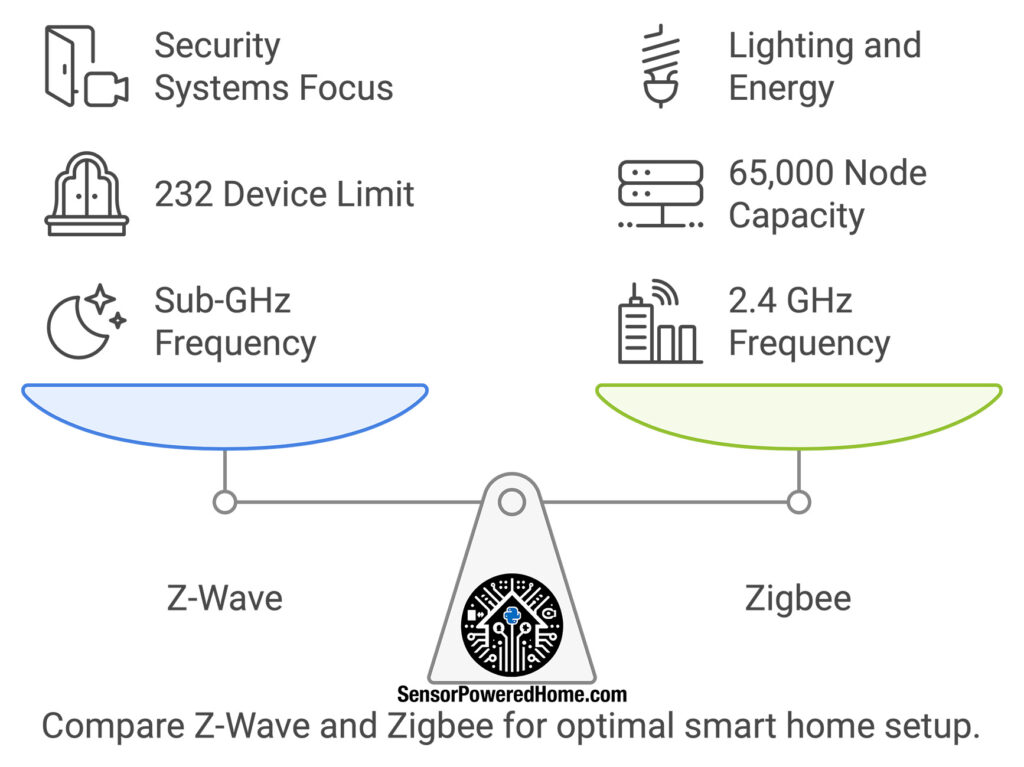
- Z-Wave: Developed in 2001 by Zensys, Z-Wave focuses on simplicity and reliability in home automation. Its hallmark feature is strict certification, which ensures seamless compatibility across devices. Think of Z-Wave as the consistent team player, perfect for structured environments like home security systems.
- Zigbee: Introduced in the early 2000s by the Zigbee Alliance (now the Connectivity Standards Alliance), Zigbee is the versatile chameleon of smart home protocols. Its scalability makes it a top choice for systems that need to manage diverse devices, from smart lighting to industrial automation.
Z-Wave shines in straightforward applications, like motion sensors for security, while Zigbee’s flexibility excels in complex setups, such as managing multi-room lighting.
Importance of Z-Wave and Zigbee in Smart Home Automation
Z-Wave and Zigbee power smart home connectivity by creating reliable mesh networks where devices function as both endpoints and relays.
- Z-Wave: Operates in the sub-GHz range, such as 908.42 MHz in North America and 868.42 MHz in Europe, minimizing interference from Wi-Fi or Bluetooth.
- Zigbee: Works on the globally recognized 2.4 GHz band, ensuring worldwide compatibility but requiring careful channel management to avoid congestion in Wi-Fi-heavy environments.
Key Differences Between Z-Wave and Zigbee Protocols
Selecting the right protocol often depends on network needs:
| Criteria | Z-Wave | Zigbee |
|---|---|---|
| Network Size | Supports up to 232 devices. | Scales up to 65,000 nodes. |
| Interoperability | Strict certification ensures reliability. | Flexible but may face implementation inconsistencies. |
| Range | Indoor range: 30–40 meters. | Indoor range: 10–20 meters. |
Pro Tip: For large-scale systems like industrial automation or energy management, Zigbee’s scalability is unmatched. For residential use, Z-Wave offers a more predictable experience. Learn more at the Zigbee Alliance.
Benefits of Using Z-Wave and Zigbee Devices in Smart Homes
Both protocols offer longevity and adaptability, allowing gradual expansion of your smart home system. Here are some key benefits of using Z-Wave and Zigbee devices:
- Reliable and Stable Networks: Z-Wave and Zigbee utilize mesh networking, where devices communicate with each other and act as relays to strengthen the overall network. This design ensures consistent connectivity throughout the home, even in large spaces.
- Minimized Interference and Efficient Communication: Z-Wave operates in the sub-GHz range, avoiding interference from Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, while Zigbee uses the 2.4 GHz band. Although Zigbee shares this band with Wi-Fi, proper channel selection and router configurations can reduce interference, ensuring dependable performance in most environments.
- Energy Efficiency: Their low-power design is ideal for battery-operated devices, such as motion sensors, door/window contacts, and remote controls, reducing maintenance and ensuring longer usage between battery changes.
- Broad Device Compatibility: Both protocols support a wide range of smart devices, from lights and locks to thermostats and security sensors. Many hubs and platforms, like SmartThings and Hubitat, facilitate cross-protocol integration, offering flexibility in device selection.
- Future-Proofing and Scalability: Z-Wave and Zigbee systems are designed for growth, enabling users to start small and expand their smart home setups over time without needing major upgrades. This adaptability ensures your smart home can evolve with your needs.
2. Understanding the Basics of Z-Wave and Zigbee Devices
Types of Devices Compatible with Z-Wave and Zigbee
Z-Wave and Zigbee technologies power a wide variety of smart home devices, catering to both simple and complex automation needs.
- Examples Z-Wave Devices:
- Motion Sensors: Detect movement to trigger alarms or lighting.
- Door Locks: Enhance security with remote locking/unlocking features.
- Smart Plugs: Monitor and control energy usage.
- Recommended Product: The Aeotec Smart Switch 7 integrates seamlessly with hubs like SmartThings, offering remote appliance control (Aeotec Smart Switch).
- Examples Zigbee Devices:
- Smart Lighting: Philips Hue bulbs allow dynamic color and brightness adjustments.
- Thermostats: Enable energy-efficient heating and cooling.
- Energy Management Systems: Provide real-time usage insights.
- Recommended Product: Philips Hue Smart Bulbs offer unmatched compatibility with Alexa or the Hue Bridge (Philips Hue Bulbs).
Troubleshooting Tip: If a device fails to pair, ensure it’s within the hub’s range and free from obstructions like thick walls or large furniture. Reset the device if necessary.
Role of Hubs and Gateways in Z-Wave and Zigbee Networks
Hubs and gateways serve as the central controllers in a smart home system, facilitating communication between devices and providing a user-friendly interface for managing automations. While both are critical for device integration, they have distinct roles:
- Hub: A hub is a hardware device that connects and manages smart devices, typically supporting multiple protocols like Z-Wave, Zigbee, or Wi-Fi. Hubs often require direct communication with devices within their network and act as a bridge to the internet for remote control.
- Gateway: A gateway is broader in function, enabling communication between different networks or protocols. For example, it may integrate Zigbee and Z-Wave devices into a larger system, like Home Assistant, while also connecting to cloud services.
How to Choose the Right Hub
- Check Compatibility:
Not all hubs support both Z-Wave and Zigbee protocols. If you’re planning a multi-protocol smart home, ensure your hub supports both for maximum flexibility. Key hubs include:
- Hubitat Elevation:
- Compatibility: Fully compatible with Z-Wave and Zigbee devices, as well as platforms like Home Assistant and openHAB through integrations.
- Key Features: Advanced local processing, high customization, and no reliance on cloud services, ensuring faster response times and better privacy.
- Best For: Power users who prefer full control and flexibility.
- Learn more.
- SmartThings Hub:
- Compatibility: Supports Z-Wave and Zigbee devices. While not directly compatible with Home Assistant or openHAB, it can connect via third-party integrations like MQTT.
- Key Features: Beginner-friendly, with an intuitive app and cloud-based processing for easy setup.
- Best For: Beginners and those who prefer simplicity.
- Learn more.
- Cheaper Alternatives:
- Aeotec Smart Home Hub: A more affordable option, compatible with SmartThings and supports Z-Wave and Zigbee devices.
- Sonoff Zigbee 3.0 Dongle: Budget-friendly and ideal for Zigbee-focused setups when used with platforms like Home Assistant.
- Ease of Management:
Look for hubs with intuitive apps for grouping devices, setting schedules, and managing automations. Cloud-based hubs like SmartThings offer simpler interfaces, while local-processing hubs like Hubitat provide more control but require a learning curve. - Future Scalability:
Choosing a hub that supports both Z-Wave and Zigbee ensures you can add new devices without compatibility issues. Gateways like Home Assistant or openHAB can expand your setup further by integrating additional protocols (e.g., Thread, Bluetooth).
Device Communication: Mesh Networking Explained
Mesh networking forms the backbone of Z-Wave and Zigbee device communication, offering reliable coverage and redundancy.
How Mesh Networks Work:
- Z-Wave:
- Supports up to 4 signal hops between the hub and devices, minimizing latency.
- Ideal for controlled setups like single-family homes.
- Zigbee:
- Allows infinite hops, making it highly scalable but requiring careful channel management to avoid interference with Wi-Fi.
Practical Example: A Zigbee motion sensor at the far end of a home communicates with the hub via a nearby Zigbee smart plug, ensuring uninterrupted performance.
Troubleshooting Tip: Weak connections? Add a repeater like a Z-Wave extender or a Zigbee smart plug to strengthen the mesh network.
3. Preparing for Setup
Checklist of Tools and Resources Needed for Setup
Preparation is the foundation of a seamless smart home experience. Having the right tools and resources ready saves time and ensures a smooth setup process.
Essentials:
- Hub and Gateway:
- For dual-protocol setups, choose:
- openHAB or Home Assistant for customization and scalability (openHAB Documentation, Home Assistant Setup).
- Aeotec Smart Hub (Z-Wave) or Aqara Hub (Zigbee) if you plan to use only Z-Wave or Zigbee.
- Hubitat Elevation, SmartThings Hub, Aeotec Smart Home Hub or Sonoff Zigbee 3.0 Dongle if you plan to use both Z-Wave and Zigbee protocols.
- Smart Devices:
- Examples:
- Sonoff Zigbee Motion Sensor for affordable motion detection.
- Zooz Z-Wave Smart Plug for energy monitoring and automation.
- Diagnostic Tools:
- Zigbee2MQTT and Z-Wave JS to visualize and monitor network health (Zigbee2MQTT Docs, Z-Wave JS Guide).
- Mobile Apps:
- Ensure compatibility with your hub for device pairing and control.
- Reliable Network Setup:
- A stable Wi-Fi connection or Ethernet for hubs. Consider dedicated networks for IoT devices to avoid interference.
Pro Tip: If using a Raspberry Pi as your hub, ensure a reliable power source and at least 16GB of storage.
Understanding Your Home’s Network Layout
Planning your network layout ensures robust connectivity and smooth performance.
Steps to Optimize:
- Centralize the Hub:
- As much as possible, place the hub in the middle of your home to distribute signals evenly. Avoid placing it near metal objects, thick walls, or Wi-Fi routers.
- Map Device Placement:
- Create a floor plan with device locations, ensuring they are within mesh range of each other (30-40 meters for Z-Wave and 10-20 meters for Zigbee).
- Address Obstacles:
- Use repeaters like Zigbee smart plugs or Z-Wave extenders to overcome barriers such as walls and furniture.
Troubleshooting Tip: Overlapping Wi-Fi and Zigbee channels can cause interference. Use non-overlapping Wi-Fi channels (e.g., 1, 6, or 11) for smoother performance.
4. Advanced Configuration Options
Customizing Device Settings
After installing and pairing your Zigbee and Z-Wave devices, optimizing their settings ensures they meet your specific needs. Tailored configurations enhance functionality and make your smart home system more intuitive and efficient.
Step-by-Step Instructions:
- Access Device Settings:
- Use your hub’s app to locate the paired device and open its settings.
- Platforms like openHAB and Home Assistant offer in-depth configuration options. For example:
- In openHAB, navigate to the “Things” menu to adjust device parameters (openHAB Device Guide).
- In Home Assistant, access settings via the dashboard or YAML configuration (Home Assistant YAML Setup).
- Modify Key Parameters:
- Motion Sensors: Adjust motion sensitivity to avoid unnecessary triggers, such as those caused by pets.
- Smart Lights: Configure brightness and color temperature for specific times of day. For example, set cool light in the morning and warm light in the evening.
- Thermostats: Define heating and cooling thresholds. Combine with temperature sensors for precise climate control.
- Test Adjustments:
- After modifying settings, test the device to confirm proper functionality. For instance, check that motion sensors trigger lights only within the specified range.
Practical Example: Adjusting the motion detection range on a Sonoff Zigbee sensor in a garage reduces false alarms caused by small animals while maintaining effective coverage.
Troubleshooting Tip: If settings aren’t applied, ensure both the hub and device firmware are up to date. Restart the hub to resolve synchronization issues.
Setting Up Automations and Routines
Automations transform your smart home into a cohesive ecosystem, connecting devices to operate seamlessly together.
Examples of Automations:
- Lighting Schedules:
- Use a Zigbee motion sensor to trigger Z-Wave lights in hallways at night.
- Program smart bulbs to gradually brighten in the morning for a natural wake-up routine.
- Energy-Saving Routines:
- Pair a Z-Wave thermostat with a Zigbee temperature sensor to optimize energy use.
- Automatically turn off unused devices if no motion is detected for a set period.
- Security Enhancements:
- Configure motion sensors to trigger cameras or send alerts during specific hours.
- Pair door sensors with smart locks for real-time notifications of unauthorized access.
How-To:
- openHAB: Create automations using the Blockly visual editor or DSL rules (openHAB Automation Guide).
- Home Assistant: Define triggers and actions using the automation editor or YAML configuration (Home Assistant Automation Editor).
Troubleshooting Tip: Ensure devices involved in the automation are online. Use diagnostic tools to verify connectivity and rule execution.
Integrating Z-Wave and Zigbee with Other Platforms
Expanding your system with third-party integrations unlocks additional functionality.
Step-by-Step Instructions:
- Choose an Integration Platform:
- openHAB: Ideal for advanced users requiring extensive customizations (openHAB Add-ons).
- Home Assistant: Offers a user-friendly interface and numerous pre-configured integrations (Home Assistant Integrations).
- Combine Protocols:
- Use Zigbee2MQTT for Zigbee devices and Z-Wave JS for Z-Wave devices to centralize control.
- Create Cross-Protocol Automations:
- Example: A Zigbee motion sensor triggers a Z-Wave smart plug to power a fan when movement is detected.
Security Consideration: Always keep hubs and devices updated to mitigate vulnerabilities.
5. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Smart home systems, while convenient, can occasionally face technical hiccups. Whether it’s connectivity issues or pairing problems, troubleshooting efficiently ensures your Z-Wave and Zigbee devices operate smoothly.
Troubleshooting Pairing Problems
When devices fail to pair, the solution is often straightforward. A systematic approach can resolve most issues quickly.
Step-by-Step Instructions:
- Reset the Device:
- Many devices have a reset button or sequence. For example, toggle a smart plug’s button three times to reset it.
- Refer to the user manual for specific steps.
- Restart the Hub:
- Power cycle the hub by unplugging it for 30 seconds and plugging it back in. This clears temporary glitches.
- Re-initiate Pairing:
- On your hub’s app, select “Add Device” or enable pairing mode. For Z-Wave devices, ensure the hub is in “Inclusion Mode.”
Resolving Connectivity Issues
Devices disconnecting or responding intermittently can disrupt your smart home system. Addressing these issues strengthens the network.
Step-by-Step Instructions:
- Test Signal Strength:
- Use diagnostic tools like Zigbee2MQTT or Z-Wave JS to check signal strength and network routes (Zigbee2MQTT Documentation, Z-Wave JS Guide).
- Reinforce the Mesh Network:
- Add mains-powered devices like Zigbee smart plugs or Z-Wave repeaters to act as relays.
- Position repeaters to bridge gaps in the network.
- Relocate Devices:
- Move devices away from thick walls, metal objects, or appliances that can block signals.
Practical Example: Adding a Zigbee plug between a distant sensor and the hub can significantly improve signal reliability.
Troubleshooting Tip: Avoid placing devices near potential sources of interference, such as microwaves or cordless phones.
Managing Wi-Fi and Zigbee Interference
Both Wi-Fi and Zigbee use the 2.4 GHz band, leading to potential interference. Adjusting settings can mitigate conflicts.
Step-by-Step Instructions:
- Change Zigbee Channels:
- Access your hub’s settings and select a less crowded Zigbee channel (e.g., 15, 20, or 25). Save and restart the hub.
- Optimize Wi-Fi Channels:
- Use a Wi-Fi analyzer app to identify the least congested channels. Channels 1, 6, and 11 are ideal for non-overlapping signals.
- Separate Networks:
- Dedicate a Wi-Fi SSID for IoT devices, ensuring minimal overlap with Zigbee channels.
Diagnosing Mesh Network Weaknesses
A robust mesh network ensures seamless communication, but weak spots can emerge.
Step-by-Step Instructions:
- Map the Network:
- Use Zigbee2MQTT or Z-Wave JS to visualize device connections and identify weak links.
- Strengthen the Mesh:
- Add strategically placed repeaters to bolster the network.
- Replace Bottleneck Devices:
- Battery-operated devices often don’t relay signals. Replace them with mains-powered devices in critical locations.
Real-World Example: Placing a Zigbee extender near a frequently disconnecting device can stabilize its connection.
Troubleshooting Tip: Regularly review your network map to detect and address emerging weak spots.
6. Ensuring Network Security
A secure smart home system is essential for protecting your data, devices, and privacy. By implementing robust security measures, you can safeguard against unauthorized access and ensure a trustworthy ecosystem.
Securing Z-Wave and Zigbee Devices Against Threats
Z-Wave and Zigbee protocols offer built-in security features, but enabling and properly configuring these features is crucial.
Step-by-Step Instructions:
- Enable Encryption:
- Use S2 (Security 2) encryption for Z-Wave devices during pairing. This feature significantly enhances data security and prevents signal interception.
- Zigbee 3.0 devices have encryption enabled by default, ensuring secure communication.
- Authenticate Devices:
- Purchase devices from reputable manufacturers to minimize vulnerabilities. Avoid generic or uncertified devices.
- Limit Device Access:
- Set device permissions on your hub to allow only trusted users and restrict access to critical devices like smart locks or cameras.
Practical Example: Pairing a Z-Wave door lock with S2 encryption ensures that signals cannot be intercepted or manipulated by unauthorized parties.
Troubleshooting Tip: If encryption is not available during pairing, update the firmware on both the hub and the device.
Setting Strong Passwords and Enabling Encryption Protocols
Your smart home hub and Wi-Fi router are critical access points for your system. Securing them prevents unauthorized control and data breaches.
Step-by-Step Instructions:
- Set Strong Passwords:
- Use a unique, complex password for your hub and router, incorporating uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Consider using a password manager like LastPass or Bitwarden to store and generate secure credentials.
- Enable WPA3 Encryption:
- Access your router’s settings and activate WPA3 encryption for the highest level of Wi-Fi security.
- If WPA3 is unavailable, use WPA2-PSK with a strong password for IoT devices.
- Secure Hub Interfaces:
- Activate HTTPS for openHAB or Home Assistant hubs to ensure encrypted communication (openHAB HTTPS Setup, Home Assistant 2FA Guide).
Pro Tip: Use two-factor authentication (2FA) on hubs and critical apps for an additional layer of security.
Regularly Updating Firmware for Devices and Hubs
Firmware updates are essential for keeping devices secure against vulnerabilities and improving performance.
Step-by-Step Instructions:
- Check for Updates:
- Use the hub’s app to check for firmware updates for both the hub and connected devices.
- Update Devices Safely:
- Ensure the device is powered on and connected during the update process. Complete updates one at a time to avoid network congestion.
- Test Functionality Post-Update:
- Verify that devices function as expected after updating.
Troubleshooting Tip: If a device fails to update, restart it and try again. Persistent issues may require assistance from the manufacturer.
Isolating Z-Wave and Zigbee Devices on a Separate Network
Segmenting IoT devices from your primary network limits the exposure of sensitive data and minimizes potential breaches.
Step-by-Step Instructions:
- Set Up a Guest Network:
- Create a separate SSID for IoT devices via your router’s settings. Use WPA2-PSK or WPA3 encryption.
- Implement VLANs for Wired Devices:
- For hubs connected via Ethernet, configure VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) on your router to isolate IoT traffic. Routers like Ubiquiti’s UniFi series simplify VLAN setups (UniFi VLAN Guide).
- Restrict Internet Access for Local Devices:
- Block internet access for devices that don’t require cloud services through your router’s firewall settings.
Security Tip: Avoid mixing high-security devices, like smart locks, with less secure IoT gadgets on the same network.
7. Real-World Use Cases
Z-Wave and Zigbee technologies are cornerstones of practical smart home applications, enabling seamless automation and significant convenience. Below are some real-world use cases demonstrating their versatility, along with actionable steps for implementation.
Home Security with Sensors and Cameras
Smart home security relies heavily on Z-Wave and Zigbee devices for reliable monitoring and automated responses.
Step-by-Step Use Case:
- Install Door/Window Sensors:
- Deploy Z-Wave sensors, such as the Aeotec Door/Window Sensor, at all key entry points. These sensors send real-time alerts when a door or window is opened (Aeotec Door/Window Sensor).
- Pair Motion Sensors:
- Use Zigbee motion sensors like the Aqara Motion Sensor to monitor hallways or outdoor areas. These sensors can trigger lights or alarms during unexpected activity.
- Integrate Cameras:
- Combine motion sensors with a smart camera system. For instance, when motion is detected, a camera begins recording and sends an alert to your phone.
Troubleshooting Tip: If alerts are delayed, check the connection strength of the motion sensor and reposition it if necessary.
Smart Lighting and Energy Management
Efficient lighting and energy management contribute to convenience and cost savings in a smart home.
Step-by-Step Use Case:
- Install Smart Bulbs:
- Use Zigbee smart bulbs like Philips Hue in frequently used rooms. Program these bulbs to adjust brightness based on time or motion (Philips Hue Smart Bulbs).
- Add Smart Plugs:
- Deploy Z-Wave smart plugs for energy monitoring and control of appliances such as space heaters and coffee makers.
- Create Automation Routines:
- Pair Zigbee motion sensors with Z-Wave plugs to activate lights or appliances only when movement is detected, reducing unnecessary energy usage.
Real-World Example: Zigbee bulbs in a living room dim automatically at sunset, while Z-Wave smart plugs power off appliances after 10 PM to conserve energy.
Troubleshooting Tip: For unresponsive smart plugs, ensure they are within range of the Z-Wave hub or add a repeater.
8. Tools and Apps for Managing Z-Wave and Zigbee Networks
Managing Z-Wave and Zigbee networks efficiently requires reliable apps and tools for device configuration, troubleshooting, and optimization. These resources simplify network management and enhance the smart home experience.
Recommended Apps for Device Management
Smart home apps offer intuitive interfaces for controlling and monitoring devices, ensuring a streamlined setup process.
Top Apps:
- SmartThings App:
- Beginner-friendly, the SmartThings app supports Z-Wave and Zigbee devices with an easy setup and automation process.
- Example Use: Schedule Zigbee lights to dim at night and brighten in the morning automatically.
- Troubleshooting Tip: If devices fail to appear, verify hub compatibility and update the firmware.
- Hubitat Elevation Interface:
- Tailored for advanced users, Hubitat provides local processing for fast automations and robust privacy. Its dashboard offers granular control over Z-Wave and Zigbee networks.
- Example Use: Use Rule Machine to create advanced routines, such as syncing Z-Wave blinds and Zigbee lights at specific times.
- Pro Tip: Use device logging to identify and resolve performance issues.
- openHAB and Home Assistant Apps:
- Open-source platforms supporting extensive integrations. The apps allow remote monitoring and adjustments for connected devices.
- Example Use: Check the status of a Z-Wave thermostat and Zigbee temperature sensor from one unified dashboard.
Tools for Monitoring and Optimizing Networks
Specialized tools provide detailed insights into network health, device performance, and connectivity issues.
Essential Tools:
- Zigbee2MQTT:
- An open-source tool that maps Zigbee networks, showing device connections and identifying weak links.
- Example Use: Diagnose connectivity issues for a motion sensor far from the hub (Zigbee2MQTT Documentation).
- Z-Wave JS in Home Assistant:
- Offers a detailed view of Z-Wave networks, including routing paths and latency.
- Example Use: Identify and resolve bottlenecks in a network with many connected devices (Z-Wave JS Guide).
- Wireshark with Zigbee Sniffer:
- Advanced diagnostic tool for monitoring Zigbee traffic and detecting interference.
- Pro Tip: Use this tool to pinpoint overlapping Wi-Fi and Zigbee channels causing interference.
Real-World Example: If a Zigbee motion sensor frequently disconnects, Zigbee2MQTT can reveal whether it’s routing through a weak node. Adding a repeater near the sensor resolves the issue.
9. Conclusion
Congratulations on completing this comprehensive guide to setting up and managing Z-Wave and Zigbee devices! With the insights and tools provided, you now have the foundation to create a seamless, secure, and efficient smart home ecosystem tailored to your needs.
Recap of Key Takeaways
- Preparation:
- Start with the right tools, hubs, and a clear understanding of your network layout to ensure a smooth setup.
- Device Pairing:
- Follow protocol-specific pairing steps for Z-Wave and Zigbee devices to integrate them into your smart home.
- Network Optimization:
- Enhance performance through mesh networking, channel management, and the strategic placement of repeaters.
- Advanced Configurations:
- Customize device settings and build powerful automations for efficiency, convenience, and innovation.
- Security Practices:
- Protect your system with encryption, strong passwords, regular updates, and segmented networks.
Encouragement for Further Exploration
The smart home journey is filled with opportunities to enhance your living experience. Z-Wave and Zigbee technologies are adaptable and scalable, offering endless possibilities for expansion and innovation.
Next Steps:
- Experiment with New Automations:
- Combine protocols to create unique workflows, such as using Zigbee motion sensors to activate Z-Wave smart lights.
- Expand Your System:
- Start with cost-effective options like Zigbee plugs or Z-Wave temperature sensors and gradually integrate advanced devices like thermostats or security systems.
- Explore Advanced Platforms:
- Platforms like openHAB and Home Assistant allow for greater customization, scripting, and cross-platform integration.
Pro Tip: Regularly review your setup as technology evolves. Firmware updates and new integrations ensure your system remains efficient and secure.
Resources for Continued Learning
Expand your expertise with these valuable resources:
- Online Communities:
- openHAB Community: Share experiences and find solutions (openHAB Community).
- Home Assistant Forum: Explore innovative ideas and troubleshoot issues (Home Assistant Community).
- Documentation and Tutorials:
- Zigbee2MQTT Guide: Manage your Zigbee network effectively (Zigbee2MQTT Docs).
- openHAB Tutorials: Learn from detailed guides for beginners and advanced users (openHAB Documentation).
- YouTube Channels:
- Channels like Everything Smart Home and DrZzs offer step-by-step video tutorials for smart home enthusiasts.
Final Thoughts
Smart home technology transforms how we interact with our living spaces. From energy management to enhanced security, Z-Wave and Zigbee devices offer the tools to create a truly intelligent home. The journey doesn’t stop here—continuous exploration and innovation will unlock the full potential of your setup.
Closing Advice: Stay curious and connected. Engage with the smart home community to learn new techniques, share experiences, and maximize your system’s capabilities. Your home is a canvas for innovation—make it uniquely yours.
FAQ Section
Q1: Can Z-Wave and Zigbee devices work together?
Yes, hybrid hubs like SmartThings or Home Assistant support both protocols, allowing cross-protocol automation.
Q2: How can I improve my network’s reliability?
Use repeaters to strengthen weak signals, avoid channel conflicts, and update firmware regularly.
Q3: Are Z-Wave and Zigbee devices secure?
Yes, with proper encryption (Z-Wave S2 and Zigbee 3.0), strong passwords, and segmented networks, they are highly secure.
Q4: What’s the best starting point for beginners?
A dual-protocol hub like Hubitat Elevation or SmartThings, combined with affordable devices like Zigbee plugs or Z-Wave sensors.
